Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
14 Jan 2015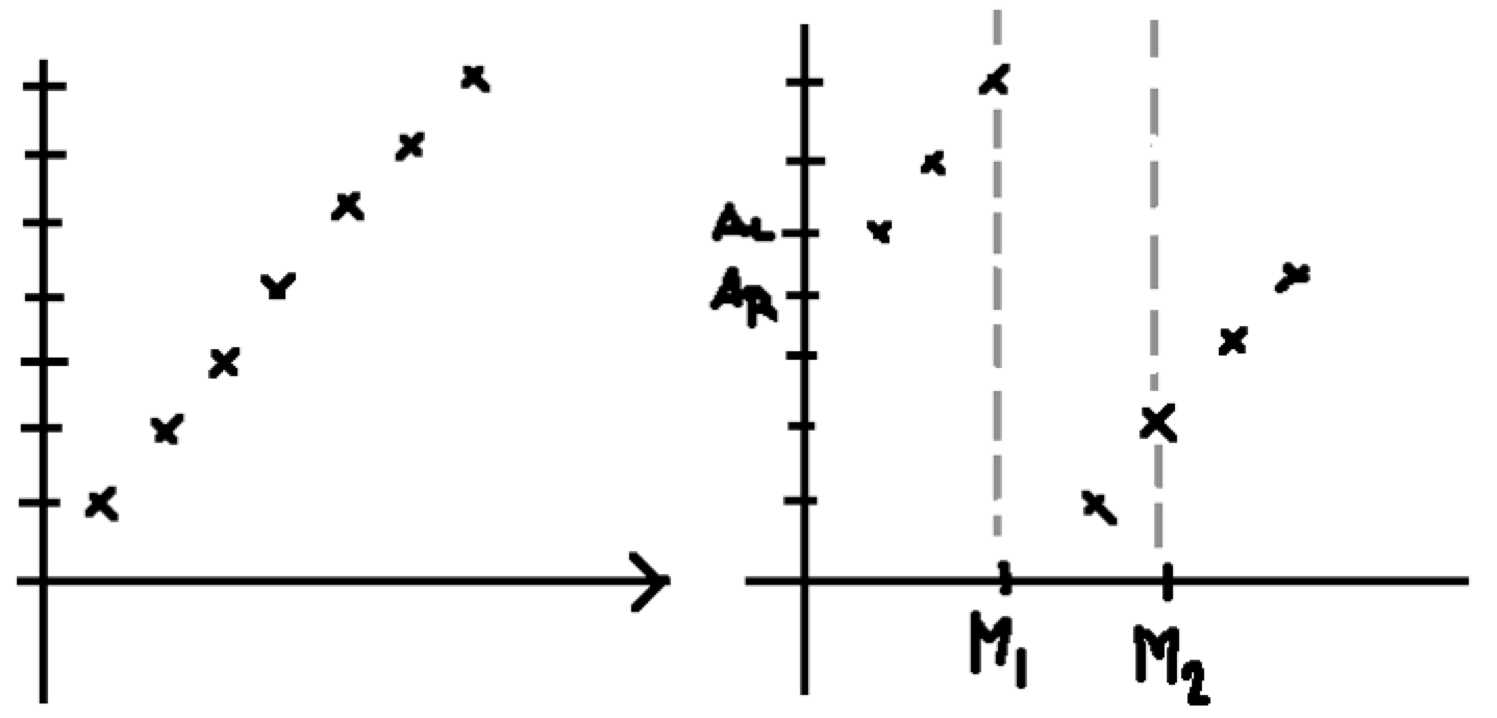
Imagine we have an array [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], See graph 1 which was being rotated 3 steps to the right [5,6,7,1,2,3,4] ,See graph 2. Let’s say we subdivide the array at point k to two subarrays [AL, AL+1, …, Ak], [Ak+1, …, AR].
If the sorted array is not rotated, then AL < AR then we could return AL as the minimum immediately.
Otherwise for a sorted array that was rotated at least one step, AL must always be greater than AR.
Let’s assume we choose M1 as the dividing point. Since AM1 > AR, we know that each element in [AL … AM1] is greater than AR (Remember that AL > AR?). Therefore, the minimum value must locate in [AM1+1 … AR].
On the other hand, let’s assume we choose M2 as the dividing point. Since AM2 ¬≤ AR, we know that each element in [AM2+1 … AR] is greater than AM2. Therefore, the minimum point must locate in [AL … AM2].
As we are discarding half of the elements at each step, the runtime complexity is O(log n).
To understand the correct terminating condition, we look at two elements. Let us choose the lower median as M = (L + R) / 2. Therefore, if there are two elements, it will choose AL as the first element.
There are two cases for two elements:
A = [1,2]
B = [2,1]
For A, 1 < 2 => AM < AR, and therefore it will set R = M => R = 0.
For B, 2 > 1 => AM > AR, and therefore it will set L = M + 1 => L = 1.
Therefore, it is clear that when L == R, we have found the minimum element.
public int findMin(int[] num) {
int n = num.length;
int end = n-1;
int start = 0;
if(num==null||n==0) return 0;
if(n==1) return num[0];
while(start<end)
{
int mid = (start+end)/2;
if(mid>0 && num[mid-1]>num[mid]) return num[mid];
if(num[mid]>num[end]) start = mid+1;
else end = mid-1;
}
return num[start];
}
Refrence :
https://oj.leetcode.com/